beta decay example|beta decay example problems : Bacolod Learn about beta decay, a type of radioactive decay in which a proton or a neutron transforms into the other inside the nucleus. See examples of . The UK 49's daily Lunchtime and Teatime results are updated here every afternoon and evening once the winning numbers have been drawn. Latest Result. Wednesday 4 September 2024 . following Smart Pick Prediction for the UK49’s Lunchtime and Teatime draws have been generated based on analysis of previous drawn numbers. These .
beta decay example,Learn about beta decay, a type of radioactive disintegration that involves the emission of electrons, positrons, or capture of electrons by nuclei. Find out how beta decay affects the atomic number and mass number of the nuclei and see examples of beta .

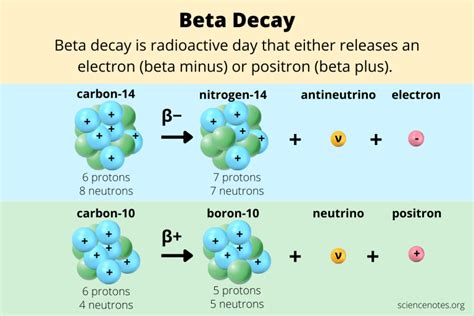
Learn about beta decay, a type of radioactive decay in which a proton or a neutron transforms into the other inside the nucleus. See examples of .beta decay example beta decay example problemsLearn about beta decay, a type of radioactive decay in which a proton or a neutron transforms into the other inside the nucleus. See examples of .In nuclear physics, beta decay (β-decay) is a type of radioactive decay in which an atomic nucleus emits a beta particle (fast energetic electron or positron), transforming into an isobar of that nuclide. For example, beta decay of a neutron transforms it into a proton by the emission of an electron accompanied by an antineutrino; or, conversely a proton is converted into a neutron by the emission of a positron with a neutrino in so-called positron emission. Neither the beta particle nor .beta decay example problems An example of beta minus decay is the decay of carbon-14 into nitrogen-14. 614 C → 714 N + e – + ν e. Other examples of beta emitters include strontium -90, tritium, phosphorus-32, and nickel-63. β .Learn what beta decay is and how it occurs in unstable atoms. See examples of β- and β+ decay with carbon-14 and carbon-10 isotopes.
The beta decay is a radioactive decay in which a proton in a nucleus is converted into a neutron (or vice-versa). In the process the nucleus emits a beta particle .
beta decay exampleBeta decay is a type of radioactive nuclear decay. In it a beta particle (fast-energetic electron or positron) is released from an atomic nucleus, converting the initial nuclide into an isobar of that nuclide.
Learn about beta decay, a type of radioactive decay where a neutron or a proton in an unstable nucleus transforms into the other and emits a beta particle and a neutrino. Watch a video and see examples of beta-minus and beta-plus decay, and read comments and .Learn about beta decay, a type of radioactive transformation that involves the emission of an electron or a positron from the nucleus of an atom. See examples, equations, and diagrams of beta decay and its effects on .The decay of technetium-99, which has too many neutrons to be stable, is an example of beta decay. A neutron in the nucleus converts to a proton and a beta particle. The nucleus ejects the beta particle and some . By Anne Marie Helmenstine, Ph.D. β - decay occurs when an electron is the beta particle. An atom will β - decay when a neutron in the nucleus converts to a proton by the following reaction. Here X is the parent atom, Y is the daughter atom, Z is the atomic mass of X, and A is the atomic number of X: Z X A → Z Y A+1 + e - + antineutrino.
Cobalt-60. The cobalt-60 isotope undergoes beta decay with a half-life of 5.272 years. Cobalt-60 decays to Nickel-60 plus an electron and an electron antineutrino. The decay is initially to a nuclear excited state of Nickel-60 from which it emits either one or two gamma ray photons to reach the ground state of the Nickel isotope. This .Beta decay is the loss of an electron from the nucleus of an atom. In Beta decay, a high-energy electron (called a beta particle) is emitted from a neutron in the nucleus of a radioactive atom. That neutron may be .
Beta \((\beta)\) decays increase the atomic number, as indicated by the blue arrows. The series ends at the stable nucleus Pb-206. An example of a decay whose parent nucleus no longer exists naturally is shown in Figure \(\PageIndex{5}\). It starts with Neptunium-237 and ends in the stable nucleus Bismuth-209.The decay of technetium-99, which has too many neutrons to be stable, is an example of beta decay. A neutron in the nucleus converts to a proton and a beta particle. The nucleus ejects the beta particle and some gamma radiation. The new atom retains the same mass number, but the number of protons increases to 44. The atom is now a ruthenium atom.
Examples: 1. The β- decay of carbon-14. In this example, a neutron of carbon is converted into a proton and the emitted beta particle is an electron. 2. The β+ decay of carbon-10. In this example, a proton of carbon is converted into a neutron and the emitted beta particle is a positron. To link to this Beta Decay page, copy the following . The nuclear disintegration process that emits alpha particles is called alpha decay. An example of a nucleus that undergoes alpha decay is uranium-238. The alpha decay of \(\ce{U}\)-238 is . In this beta decay, a thorium-234 nucleus has one more proton than the original nucleus. In this beta decay, a thorium-234 nucleus has become a .The electron from the beta decay of 32 P can approach the full decay energy of 1.71 MeV, but it has an average value of about 0.7 MeV. For another numerical example, consider the example of the beta decay of bismuth 210 Bi cited by Krane. For the beta decay 210 Bi .
Radioisotopes tend to favor either alpha or beta decay. However, some isotopes can undergo either alpha or beta decay. Bismuth-212 is an example. We know the decay type(s) for each radioisotope, .
For example, the Q-value of typical beta decay is: In the process of beta decay, either an electron or a positron is emitted. This emission is accompanied by the emission of antineutrino (β- decay) or neutrino (β+ decay), which share the energy and momentum of the decay. The beta emission has a characteristic spectrum.We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us.
Examples of Beta Decay. There are a number of real-life applications that make use of beta decay. Some of them are listed below: 1. Particle Physics. Beta-decay is a process that takes place at nuclear level, .
Also, note that because this was an alpha reaction, one of the products is the alpha particle, He24 He 2 4. Note that both the mass numbers and the atomic numbers add up properly for the beta decay of thorium-234 (Equation 17.3.3 17.3.3 ): mass number: 234 = 0 + 234 234 = 0 + 234. atomic number: 90 = −1 + 91 90 = − 1 + 91.One type of a nuclear reaction is radioactive decay, a reaction in which a nucleus spontaneously disintegrates into a slightly lighter nucleus, accompanied by the emission of particles, energy, or both. An example is shown below, in which the nucleus of a polonium atom radioactively decays into a lead nucleus. U235 92 → He4 2 + Th231 90.A beta particle (β) is a high-speed electron emitted from the nucleus of an atom during some kinds of radioactive decay (see Figure 11.4.2 ). The symbol for a beta particle in an equation is either β or e − 0 1. Carbon-14 undergoes beta decay, transmutating into a nitrogen-14 nucleus. C14 6 → N14 7 + e − 0 1.Beta Decay. Beta decay is a type of radioactive nuclear decay. In it a beta particle (fast-energetic electron or positron) is released from an atomic nucleus, converting the initial nuclide into an isobar of that nuclide. For example, a neutrons beta decay converts itself into a proton by emitting an electron following the anti-neutrino. The first quantitative rate theory of beta decay was given by Enrico Fermi in 1934, and the essentials of this theory form the basis of modern theory. As an example, in the simplest beta-decay process, a free neutron decays into a proton, a negative electron, and an antineutrino: n → p + e − + ν.

As beta decay was studied over the years following 1899, it was found that the same exact beta decay produced an electron with variable energies. For example, let us study Li-8 becoming Be-8. Each atom of Li-8 produces an electron and the theory says all the electrons should have the same energy. This was not the case.
beta decay example|beta decay example problems
PH0 · what happens during beta decay
PH1 · what does beta decay mean
PH2 · positive beta decay
PH3 · example of beta negative decay
PH4 · beta positive decay example
PH5 · beta decay symbol
PH6 · beta decay example problems
PH7 · beta decay calculator
PH8 · Iba pa